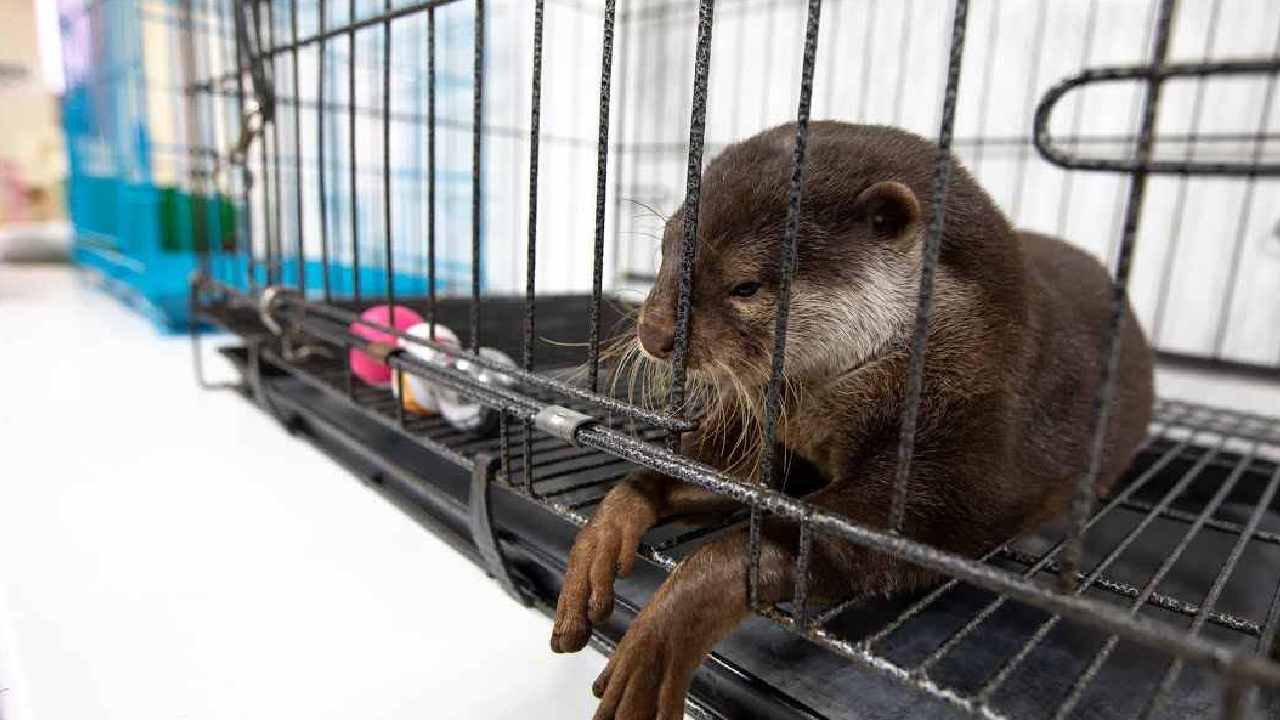
Understanding the Risks of the Exotic Pet Trade
There is a strong attraction to exotic pets. From vivid parrots to beautiful big cats, these animals fascinate us. Yet there are profound ethical, environmental and legal questions that most people gloss over. The illegal trade in exotic pets places animals, ecosystems, and even human communities in danger. This blog emphasises the risks of the illicit pet trade, the black market for exotic animals, and why some exotic pets are bad.
Many are fascinated by exotic stories, leading to their demand. But there are ethical dilemmas and dangers behind this trade. This blog will look at the pet trade, the illegal pet trade, the black market of exotic animals, and reasons why owning exotic animals may be a bad idea.
Key Benefits / Why It Matters
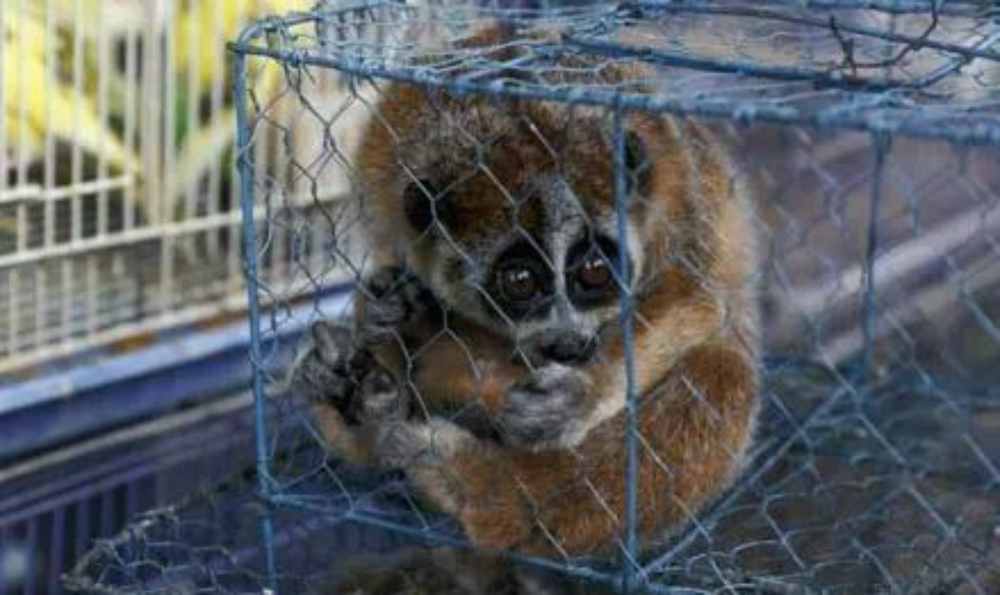

Understanding the exotic pet trade’s implications is vital for several reasons.
Ethical Considerations
Many exotic pets are taken from the wild, causing stress and harm. Wild-caught animals endure trauma during capture and transport. They often face starvation, dehydration, and injury. Young animals are taken from their mothers, making them vulnerable to illness and stress. Even those bred in captivity may suffer from poor care, as many owners lack the necessary commitment.
Impact on Biodiversity
Removing animals from their natural habitats disrupts ecosystems and threatens species with extinction. Many exotic pets are apex predators or key species that maintain ecosystem balance. For example, removing a top predator can lead to an overpopulation of prey species, resulting in habitat degradation. The pet trade has already harmed many species, such as the African grey parrot, which is now endangered due to over-extraction by the pet industry.
Public Safety Concerns
Exotic animals can pose risks to human health and safety. Some species, like large cats and primates, can be unpredictable and aggressive, leading to serious injuries or even fatalities. Many exotic animals also carry zoonotic diseases—illnesses that can transfer from animals to humans. For instance, turtles and snakes can carry salmonella, while primates can transmit herpes B and other infectious diseases.
The illegal pet trade is a multi-billion-dollar industry operating in the shadows. It involves capturing and selling animals without permits or concern for their welfare. This black market thrives on high demand and significant profits, often at the expense of animal well-being and environmental sustainability.
The Illegal Pet Trade: A Closer Look
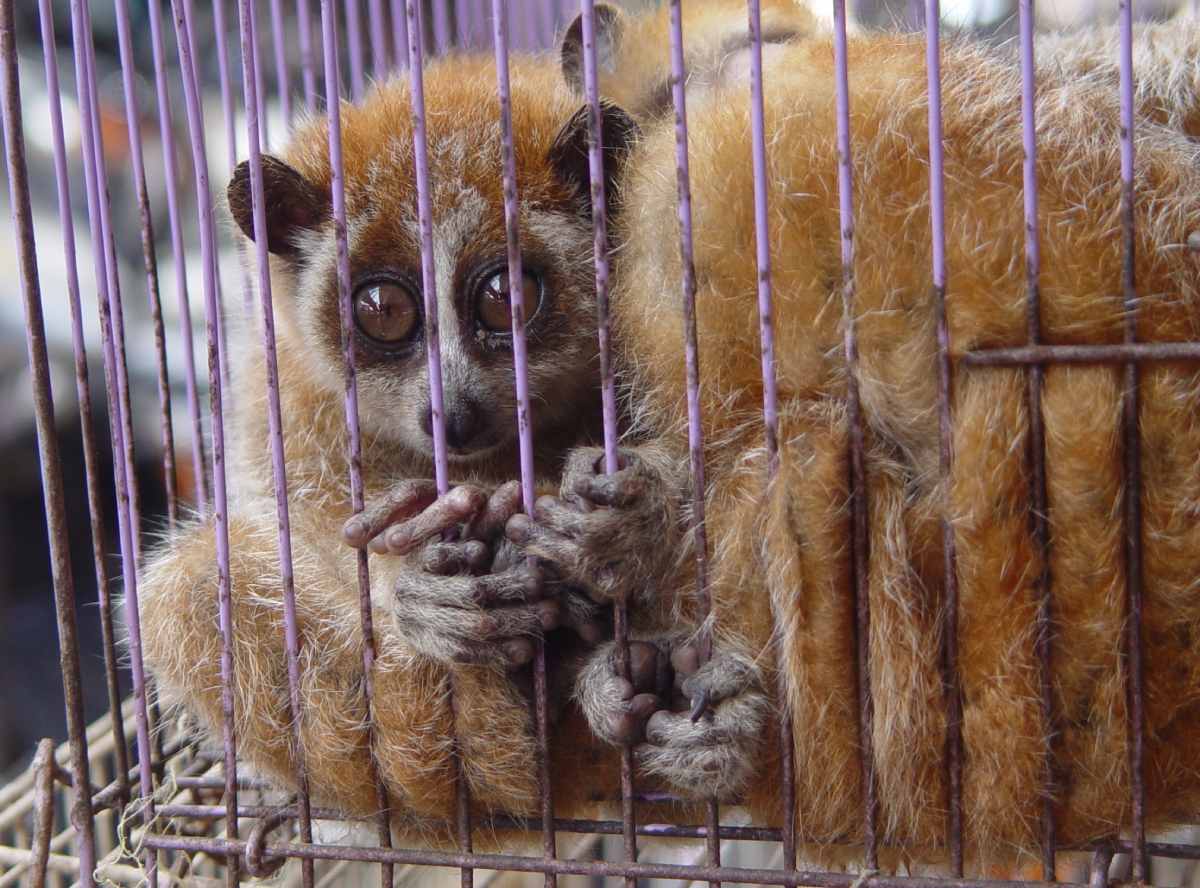

The illegal pet trade is a global issue with networks spanning continents. Animals are often smuggled across borders in terrible conditions, leading to high death rates. Many trafficked animals die from stress, suffocation, or disease before reaching their destination. This trade threatens individual animals and entire species, contributing to population declines and even extinction.
The Role of Demand in the Illegal Trade
The demand for exotic pets drives the illegal trade. Many people are attracted to the uniqueness of these animals without considering the ethical implications. This demand fuels a lucrative black market, where animals are sold with little regard for their welfare. Social media has worsened the issue, with influencers showcasing exotic pets as trendy. This leads to increased interest and higher rates of poaching and illegal sales.
Impact on Biodiversity and Ecosystems
Removing animals from their habitats can have disastrous effects on biodiversity. Many species play crucial roles in their ecosystems. Their absence can lead to imbalances and ecosystem collapse. Introducing exotic species into new environments can create invasive species problems, threatening native wildlife. For example, Burmese pythons released in the Florida Everglades have harmed native mammals by preying on them, drastically reducing their populations.
Step-by-Step Guide / Actionable Insights
For those considering owning an exotic pet, thorough research and ethical considerations are essential. Here are steps to guide potential exotic pet owners:
Research and Education
Before acquiring an exotic pet, learn about the species’ needs, habitat, and behaviour. Understanding these factors helps determine if you can provide an appropriate environment. Many exotic pets have specific needs that are hard to replicate in captivity, such as special diets and large enclosures. Not meeting these needs can lead to stress, malnutrition, and shorter lifespans.
Legal Considerations
Check local and international laws about owning exotic pets. Many species are protected by law, and owning them without permits can lead to legal trouble. The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) regulates international trade in endangered species, but enforcement varies by country. Sometimes, exotic pet ownership may be legal but requires permits, inspections, and proper habitat provisions.
Assessing Suitability
Evaluate if the species is suitable for a domestic environment. Some animals have complex needs that are hard to meet in captivity, leading to stress and health problems. Large predators, like tigers and bears, need vast spaces and specialised care, which most owners cannot provide. Even smaller species, like sugar gliders and hedgehogs, have specific dietary and environmental needs that can be tough to maintain.
Additional Expert Tips & Common Mistakes to Avoid
Experts advise against impulsive decisions when considering exotic pets. It’s crucial to consider the animal’s welfare long-term.
Common mistakes include:
- Underestimating the animal’s needs: Many people think exotic pets will behave like dogs or cats, leading to inadequate care.
- Overestimating one’s ability to care for it: Exotic animals often require lifelong commitment and specialised care.
- Buying from unverified sources: Many sellers operate illegally, fueling the black market and selling mistreated animals.
- Not considering rehoming difficulties: If an exotic pet becomes unmanageable, finding a proper new home can be challenging, and some end up abandoned.
Advanced Insights / Expert Recommendations
For those passionate about exotic animals, there are ethical ways to engage with them.
- Support conservation efforts to protect species in their natural habitats.
- Visit reputable sanctuaries that prioritise animal welfare.
- Advocate for stronger wildlife protection laws to combat illegal trade.
- Support captive breeding programs that preserve species without contributing to the illegal trade.
Understanding Exotic Pet Trades: Rectifying the Problem
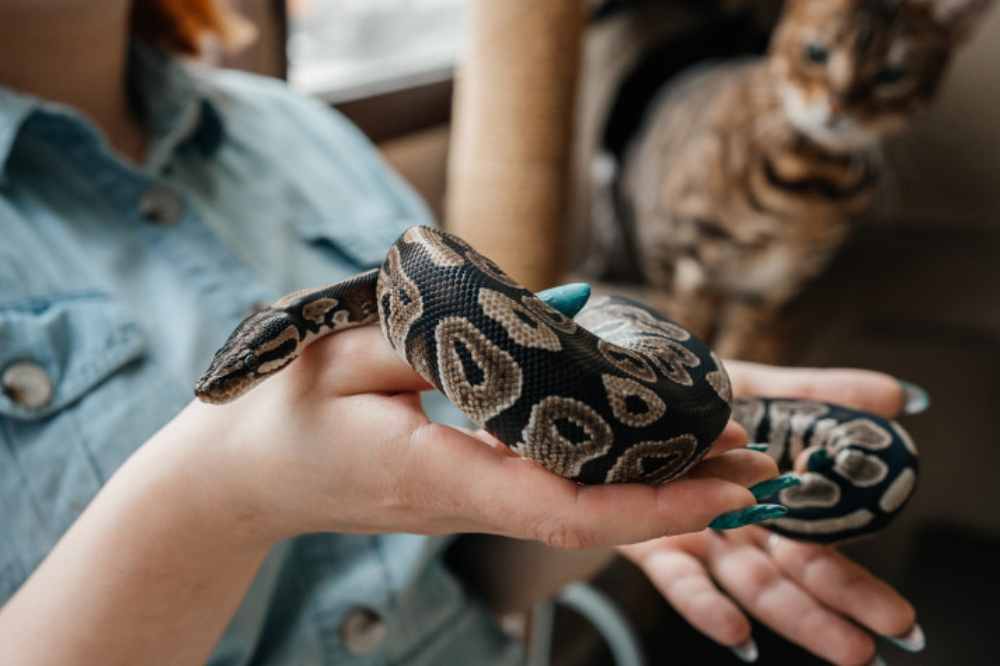

The trade-in of exotic pets is a convoluted one. It will need to understand the ethical, environmental, and legal implications. With awareness and activism, we can safeguard wildlife and protect biodiversity. If an exotic pet is something you’re thinking about, pause to read and think about the broader implications of what you decide. And, together, we can work towards a more sustainable and ethical approach to exotic pet ownership.
While we may be enamoured by exotic pets, when it comes to making such considerations, being responsible is key. By being aware of the risks and making informed decisions, we can prevent our fascination with these creatures from being detrimental to them or our planet. What actions will you take to help ethical exotic pet ownership?